What Is Warehouse Management?
A Comprehensive Guide
This Guide gives insights into everything you will ever need to know about warehousing and warehouse management. Manage your warehouse with dexterity using a warehouse management system.

WRITTEN BY
Cin7 Core | Aug 30, 2021
Table of Contents
Table of Contents


Appreciate
39What Are The Basic Warehouse Management Principles


In simple words, warehouse management refers to overlooking processes, people, and operations (including internal and the ones undertaken in collaboration with the external stakeholders.) This being said, unlike other functional departments within an organization, warehouse management requires complete synchronization with all processes and insights within the value chain to function at its best.
A warehouse is a dedicated storage facility that meets the technical and compliance guidelines laid down for storing the designated materials. Generally, it is a sizable piece of real estate, and its operations function in a distinct, specialized manner.
Despite the advent of online selling and the ever-increasing number of SKUs, there is a lack of technical know-how regarding cash flow warehouse management. Many folks confuse it with inventory management, but you should remember that inventory management is about particular items/materials. On the flip side, warehouse management is concerned with the flow and handling of inventory throughout the facility and the economics involved in the process.
What’s the difference between Warehouse Management and Inventory Management?
| Capability | Warehouse Management | Inventory Management |
| Managing the physical location of stock within a warehouse | Yes | No |
| Providing an accurate stock count across all warehouse and store locations | No | Yes |
| Required to efficiently manage orders and their delivery to customers | Yes | Yes |
| Managing stock at a single location | Yes | No |
| Reports are focused on: | Physical Inventory | Financial Component Of Managing Inventory |
| Influence of third-party stakeholders like suppliers, shipping partners as an analytical factor | More | Less |
Now we have an understanding of warehouse management and how it differs from inventory management. Let’s have a look at warehouse management principles that you can implement for utilizing your storage facility at an optimal level.
The different approaches mentioned herein will be equally applicable to all organization sizes and sectors. Of course, you will need to customize these tips based on your individual requirements, but the broader roadmap remains the same. Let’s have a quick look at them.
Make Intuition Smarter
One of the first pieces of advice we would give you is to make your intuitive smarter by feeding your brain the facts. It is in your best interest to collect data extensively, collaborate with all stakeholders, and take decisions that are well-calibrated. This will improve the quality of your operations and minimize the chances of any bottlenecks.
It is easier said than done, as warehousing requires handling complicated cascading workflows spanning multiple stakeholder interactions. The best way to optimize the process is to begin with implementing SaaS-based warehouse management software.
It will help computerized data collection and record-keeping. But the biggest benefit you will get is automating decisions revolving around warehouse management. This includes allocating storage space to incoming goods, coordinating internal stock transfers with respect to pipeline inventory, and allocating adequate manpower for concerned processes.
In a nutshell, you need to make data-driven, result-oriented decisions at each phase of operations, and automation is the only way you can maintain a high accuracy rate. Guesswork will only lead to the utilization of your resources and capabilities while unnecessarily straining your staff.
Use A Dynamic Approach To Warehouse Operations
It is noteworthy that flexibility is a powerful value proposition in today’s supply chains. Therefore, using a dynamic approach to your warehouse operations is a must. You can begin with creating a workflow diagram and assessing it against your storage space’s physical layout. This sort of auditing gives you an idea of the infrastructure level changes you might need to facilitate a smoother flow of goods.
This tip leans towards better utilization of data concerning the journey of inventory items. Thus, you must use insights from your sales department and the impact of market inputs on your procurement. Training your employees to adapt to newer working principles and equipment is equally important.
You should devise SOPs for various warehousing activities that are interoperable and keep your warehouse management system in the loop. This will help mitigate risks caused by excessive pressure on your supply chain along with sudden changes in priorities.
Implement Amazon’s “Customer-First” Inspired Approach To Warehousing Activities
Amazon has undeniably disrupted multiple sectors, and “customer-first” is the core mantra behind its approach to all its processes and goals. Warehousing is also among its most competitive aspects when it comes to its eCommerce business.
Everything needs to be designed with your customers at the center, from your storage facility’s layout to your operations and workflows. This might require you to make some major changes in the beginning, but as your business grows, everything falls in its due place, creating a seamless ecosystem with a customer-first approach.
For instance, introducing automated return merchandise authorization with prepaid return labels combined with full integration with your WMS simplifies operations while adding the much-needed predictability. Similarly, you can interweave your customer’s expected outcome in your operating procedures to give a competitive edge to your business.

Evaluate If Your Material Handling Equipment And Staff Are Up To Date
As a business grows, the type of inventory it handles starts changing rapidly and not analyzing if your material handling equipment is capable of handling new types of materials and objects. Your staff members will also need to be trained for any specific material types to make them aware of the new equipment and handling best practices.
It would be best to use a computerized WMS solution that allows you to record your material handling capacity and headcount to automate decision-making regarding work allocation. This will reduce the chances of misappropriation of your capacity to handle inventory while also allowing you to coordinate better with other departments during activities like inventory audits.
Democratise Insights Using Barcoding
We can never value enough the benefits of barcoding when it comes to managing warehouses. It is recommended to use barcodes at every phase, and if you utilize unique SKUs for your business, you should relabel incoming inventory before loading it onto your shelves. This, of course, requires integration with your warehouse software.
Barcodes can also provide you with great ease of operations during activities like internal stock transfer and reassignment of SKUs to a different product. Also, you should label your material handling equipment, including trolleys, bins, and trays, for order picking.
This will help your staff members use only designated pieces of equipment and maintain foresight of the available resources. Once the picked items arrive, you can relabel them along with the palettes for getting seamless visibility of how items “flow” through your warehouse.
Barcoding acts as a gateway for connecting the cyber and physical systems. It generates tremendous value in the form of insights and allows you to identify and address any problems both in real-time and in the future.
Emphasize Analytics: Warehouse Management Is More About Information Management
The final piece of advice we would love to extend is that warehousing has more to do with understanding data than it has to do with handling your inventory. Put simply, inventory and your storage facility are both resources, and perhaps, getting hold of data is the only way you can increase your profitability.
You should conduct a periodic audit of your warehousing operations and cross-check it with the analysis of inventory audits. The combined results will give you an idea of any possible bottlenecks along with situations where you need to rethink storage facility layout/equipment usage.
As we mentioned earlier, integrating your warehouse system with the rest of the software solutions like the inventory management tool, shipping and tracking module, sales and marketing software, CRM, procurement solutions, and accounting software allows you to see the collective picture in a real-time basis.
They will also assist you with the help of extensive dashboards, thus providing you with greater control over your operations. It also improves your ability to plan out your warehousing operations.
Warehousing in today’s time has turned into a vital business process as opposed to an obligatory process. The best practices shared here are focused on policy building and strategizing, as other pieces of advice are already available on the internet.
However, we would like to add that warehouse management is yet to witness major technological advancements like IR 4.0, 5G connectivity, and AI. They will also create newer optimization opportunities as well.
What Is Fulfillment Warehouse And Which Are The Different Kinds Of Warehouses?
The terms fulfillment center and warehouses are often confused with each other and even used interchangeably. This can be attributed to the broad similarities between the two. Fundamentally, both of them are large pieces of real estate meant to store inventory and form an important link of the modern-day supply chains.
Fact Time: The warehousing and storage market is expected to grow by a staggering $326.91 Billion during the forecast period 2020-2024.
The difference between the two lies in the services provided and, ultimately, the fashion of utilization. Read ahead to learn more about fulfillment warehouses. We all also have a quick look at the different types of warehouses. Let’s get started:
What Is A Fulfillment Center: A Quick Overview
As we discussed above, it shares a lot of qualities with a warehouse, but these aspects make it distinct from the latter:
- It is used by third-party logistics (3PL) providers and mainly caters to e-commerce supply chains.
- The dwell time for the inventory items is rather on the shorter end.
- It may hold inventory of multiple companies.
- Equipment, processes, and people are oriented towards efficient, accurate, and quick order fulfillment.
Thus, a fulfillment center is focused on delivering ‘service’ as compared to warehouses that act as infrastructure. Therefore, they are more suitable for processes like cross-docking and facilitating same-day/next-day delivery schedules.
The 3PL service providers may also come up with stock carrying levels of the same item at fulfillment centers located in different regions. This allows them to create a smart inventory relay approach that ensures optimal delivery times across all regions. In the case of returns, the item can be dispatched to the nearest fulfillment center. Thus, it helps give a competitive edge through agility.

Different Types Of Warehouses
Now that you have gone through the differences between a fulfillment center and warehouses in general let us quickly move towards warehouses’ classification. Since we have gone through fulfillment warehouses above, we will focus on other types here:
Public Warehouses
Public warehouses are owned and managed by government agencies. They can be used by private players also. The rent is usually quite affordable, and it provides a great alternative to the private companies looking for inexpensive storage options for additional inventory to meet short term. This can be equally beneficial to eCommerce store owners who are in their budding phase.
The technological support isn’t up to mark when compared with private warehouses, but the pricing offset makes up for the same. Generally, public warehouses are preferable for SMBs, and they can help provide a cushion for sudden increases in inventory holding levels. Also, organizations that cannot afford to build a dedicated storage facility find it a suitable way to store their inventory.
Private Warehouses
As the name indicates, private warehouses are owned and managed under private ownership. It can be owned by a single player or even multiple organizations in the form of pooled infrastructure. Naturally, they are more expensive, and there’s a larger list of terms and conditions attached. However, due to the technological sophistication available, you can make up for the bigger price tags depending on the applications you need.
The operations, too, lean on the competitive side, which translates to agile and accurate inventory handling. These warehouses are usually leased fully or partially by major corporations for one-off requirements or if they are in need of a temporary facility while they expand their presence. Private warehouses are equally beneficial for eCommerce companies and mid-sized organizations as they can offer competitive packages for long-term storage.
Bonded Warehouses
Bonded warehouses are typically oriented to entertain import-based goods. The inward items are stored in these warehouses until their duties are paid for, and the consignee is available at the location to accept the delivery. The concerned authorities issue bonds to compensate them since the owner doesn’t pay anything till the consignment is formally released.
Thus, they are the preferred choice for importers as they can park their consignments for extended periods without paying any duty till they receive the delivery.
One can also store items here for a longer period, and this facility is especially useful for storing restricted items. They would require additional provisions in the cases of other private facilities or entail potentially threatful legal complications.
Smart Warehouses
This category of warehouses refers to the storage facility with technically advanced solutions like a fully automated AS/RS system, robots, AI-based sales forecasting, and SaaS warehouse management software.

Large corporations use smart warehouses that need to handle gigantic inventory with a huge number of SKUs. Thus, companies like Amazon and Walmart are among the few but sizable users 0f smart warehousing technology.
Consolidated Warehouses
A consolidated warehouse is a shared storage facility that caters to short-term storage requirements from mostly eCommerce sellers. The items received should be meant to be shipped to a nearby location, and any company can use the facility for sending parcels to a particular region.
Thus, consolidated warehouses act as a consolidated solution for items that are to be shipped within a ‘common’ region.
Cooperative Warehouses
Put simply, it is a warehouse owned and managed by a cooperative society of companies and/or in association with a government/semi-government body. Usually, the cooperative society’s members use it on a mutually agreeable basis, but parties outside the co-op can also utilize it if they have the permission to do so in exchange for pre-decided fees. However, preference is given to the members in case of conflict of interest, and even among the members, space is allocated equitably.
Hazmat Warehouse
Here, Hazmat stands for hazardous materials. These facilities are specially designed to meet the storage requirements for materials that are termed potentially dangerous to human life, flora, fauna, and the overall surrounding ecosystem. Hazmat warehouses follow strict compliance requirements, and each designated material is handled safely and stored in accordance with the guidelines.
Naturally, the storage costs are higher than a regular facility, but it is indeed safer to do so. These warehouses also undergo planned checkups from local government and semi-government authorities, including surprise checkings as well.
Cold Storage
As the name indicates, cold storage provides controlled environment facilities for storing temperature-sensitive products over extended periods. They are generally used by agro products, the food industry, and the FMCG sector at large, while the chemical industry may use them as well.
The items stored here have a longer than general dwell period, and failing to maintain a controlled environment can cause inventory risks in the form of damage to its fitness for consumption. Therefore, the material handling equipment and transportation are also designed to meet the temperature and handling requirements.
Which Type Of Warehouse Is Best Fit For Your Organization
Well it depends, and no, we are not diplomatic. In fact, an organization can be using multiple types of warehouses to meet its requirements. But for utilizing your warehouses, you will need to use proper warehouse management software and train your staff to ensure operational best practices. This way, you can optimize your inventory costs sustainably without losing track of your inventory or work plans.
Warehouse Technology and Barcode Scanning Systems

Warehouse management refers to planning, organizing, and controlling the warehouse systems and the technical equipment needed to ensure intelligent warehouse logistics. Also, it assures a supportable supply chain and is a powerful medium to maintain a clear structure and order in your warehouse.
Technology is making its involvement in every sector. Whether it’s a huge retail company or a small company, information technology in warehouse management will help streamline their internal operations.
As per your company’s needs and employees’ needs, you might invest in heavy-duty equipment and machines to assist your warehouse team in managing internal processes. With the growing inventory, all the warehouse processes will become more complex. At that time, you will need the best technology for tracking your products from the warehouse to the delivery.
Warehouse technology covers goods storage and an imperative aspect of corporate logistics. Also, it functions as an interface between production, procurement, disposal, and distribution. Warehouse technology is vital for making complete surety on the materials flow.
The warehouse barcode scanner is the best warehouse technology that is used for managing your warehouse efficiently. Let’s see it in detail below –
Barcode scanning systems

A Barcode scanning system is defined as the collection of tools that permit the electronic transfer of data related to your inventory’s different products.
Standard tools used in the system include Handheld Scanners, Mobile Applications, Web Applications, Printers, and Intranet Servers. Thousands of models present; each one is designed to have a diverse set of features that will match your different specs or business wants. No matter which system for POS purchases, field service operations, inventory management, or any other purpose you want, picking the suitable barcode scanner is an imperative task.
Considering today’s standards, Laser Barcodes Scanners are the most popular type of barcode scanner.
These scanners depend on the red diode for reading the black and white markings present on the label in either a linear or an omnidirectional pattern. Those supporting omnichannel directional scannings consist of an extensive reading area and are easy to use compared to their linear counterparts.
So the Linear Imaging Barcode Scanner is capable of reading only 1D barcodes. Rather than using a laser, they opt for using image capture technology for scanning barcodes and digital image processing function for decoding them.
2D barcode scanning works differently than in the linear imagers, except they read stacked and 2D barcodes. Also, they have the capability of scanning the barcodes in any direction.
When deciding the final barcode scanner system to use in your warehouse, many confusing points come in front of us.
Let’s try to understand all such problems with their solution
Are you really in need of a scanner for the indoor and outdoor both?
All such companies that have outdoor apps must opt for barcode scanners having rugged durability. An IP rating of IP54 and IP65 shows that such a barcode scanner can endure exposure to water spray, dust, and any other environmental jeopardies.
What type of work environment do you have?
Indoor apps can exhibit devices like barcode scanners for potentially harmful diverse materials like debris, heavy dust, chemicals, and moisture. Having indoor scanning apps with possibly dangerous situations, go for an enduring model amidst an IP rating of IP54 and IP65.
How frequently will it be placed for using frequency and volume?
Are you in need of scanning hundreds of assets at a single shot that too in fast succession, or have limited scanning activity? Some barcode scanners can quickly and continuously scan up to 60-120 images/second. On the other hand, others need a few seconds to process every scan.
What are the types of symbologies that you require for scanning?
Asset tags and labels printed with different types of symbologies vary from 1D to 2D to PDF417, OCR, DPM and postal, etc. Some other barcode scanner consists of an extensive range of decoding abilities while others work with only standard 1D and 2D symbologies.
At what distance typically do you opt for scanning?
Are you scanning the badges from the ceiling, or are you scanning assets a few feet from the user? There are some kinds of barcode scanners that have the full ability to read such symbologies at larger distances compared to others.
How movable your workers are and how scatter are your assets?
Suppose your staff members are navigating all over the building area and scanning assets throughout the working day. In that case, a wireless barcode scanner is the best choice. A tethered barcode scanner is enough for retail and similar apps.
After defining your business needs, you can find out appropriate barcode scanners in detail by analyzing factors like Mobility and Bluetooth Connectivity, Power and Charging Needs, and Software Compatibility and Extra Functionality.
Warehouse Management System (WMS) – Meaning
Warehouse Management System or WMS, is software that helps you manage all your warehouse operations efficiently. A warehouse is one of the key areas of any product-based company. With the help of a WMS, you can easily oversee processes like inventory management, logistics, supply chain management, etc.
There are several kinds of warehouse management systems available in the market. Each has its advantages and shortcomings. This provides a variety of options for companies to choose from, depending on their needs and budget.
Key Features of a Warehouse Management Systems
Warehouse Slotting
Warehouse slotting is a process of reconfiguring the picking and packing workflow to optimize the warehouse operations and make them a lot more efficient. This is a very important feature because most warehouses lack a systematic approach to handle their operations.
A warehouse management system can help shorten the picking process by allocating locations to products based on their demand and sales frequency. This creates a long-term impact on the overall efficiency of a warehouse.
Real-time Inventory Tracking
Tracking your inventory in real-time allows you to keep tabs on your stock levels for all the products. A powerful WMS comes with options to track inventory using RFID and barcode scanners.
WMS uses all this information to show you the latest numbers on the dashboard. You can also get your hands on the detailed reports generated by the software.
Picking and Packing
A warehouse management system helps the user organize their picking and packing processes following models like zone picking, batch picking, wave picking, etc. This speeds up the process and optimizes the warehouse.
Shipping
WMS software also helps in generating important shipping documents like the bill of lading, packing list, shipping labels, etc. These documents play a vital role in logistics management and ensuring quality customer service.
Reporting
With the help of a powerful Warehouse Management System, you can quickly get your hands on a wide range of reports and analyses. These reports are created by using the data that is fed into the software from different operations across your warehouse.
These reports help an organization run its warehouses systematically, identify potential problems well in advance and mitigate the risks. Eventually, all of this leads to a significant jump in the overall efficiency and profitability of the company.
Types of Warehouse Management Systems
On-Premise
An on-premise warehouse management system is a type of WMS that is installed on a local server located within the premises of the company. It functions as a stand-alone system and doesn’t need any external connectivity.
Generally considered as the lowest priced option, on-premise warehouse management systems come with their own sets of advantages and disadvantages. Let’s take a look at what their strengths and weaknesses are:
Advantages:
- Full control over every aspect, from design and development to features and functionality.
- Only pay for the features you need.
- No subscription costs. Just a one-time installation fee and regular maintenance costs.
- Ownership over the software.
Disadvantages:
- Very difficult to scale up or down.
- Requires in-house experts to maintain the software and the setup.
- Data security is a primary concern since it is much more vulnerable to hacking due to local security features.
- Not ideal for growing businesses.
Cloud-Based WMS
Cloud-based warehouse management systems are, in many ways, everything that the on-premise ones can’t be. They’re systems that are stored on a remote server and are made available to companies at a fraction of the cost of development.
Companies who opt for cloud-based WMS have to pay a monthly/yearly subscription cost that depends on the type of features they select. It’s a robust software that provides cutting-edge technology to companies without having to spend a lot of money upfront.
Here are some of the advantages and disadvantages of cloud-based WMS:
Advantages
- Only pay for as long as you want the software. No extravagant up-front costs.
- Can scale up or down very easily.
- Since the security is managed by the service provider, your data is much more secure.
- Cloud-based WMS comes with a rich user experience and is easy to operate.
- Quicker implementation.
Disadvantages
- Less control over the design and development.
- No ownership.
- Costlier in the long term, compared to the on-premise WMS.
Advantages of using a Warehouse Management System (WMS)

Seeing the rise in e-commerce and customers’ demand for separate front-door deliveries, getting the inventory at the correct location is imperative. Choosing the right warehouse management system will assist you in obtaining huge success.
There is a long list of warehouse management system advantages, have a look at it
It helps to diminish operating costs

A feature-loaded warehouse management system has the full potential to reduce your operating expenses. It can be done in many ways and helps to find out the correct use of space and labor for reducing waste. The WMS software resolves the problem of keeping products, materials, and equipment for optimizing the warehouse flow.
Also, there are some kinds of advanced systems that consist of warehouse floor simulators. These simulators allow users to build a potential plan for the floor in the system. The role of the simulator also reflects in placing the pallets, equipment, and shelves to accommodate them in the warehouse.
Tremendous visibility in the inventory

The role of inventory management is significant in warehouse management. The modern warehouse management system helps in boosting the visibility of your inventory. Real-time data allows handling the entire inventory via barcodes, radiofrequency identification, and serial numbers. All these help in effective tracking of the movement of your products while transportation.
By tracing products, you can find spoiled or damaged goods, broken batches and recall them. The other advantage of inventory visibility is JIT (Just-in-time) inventory management. It ensures rapid and safe inventory flow in between the warehouses and deliveries.
Accurate demand forecasting is responsible for generating optimal inventory levels. This method will help diminish safety stock and carrying costs that will boost revenue and reduce waste.
More agile inventory turnover
If you are thinking of improving your warehouse and business processes, you must enhance your whole inventory management work. With the help of inventory management, you can keep complete control of your inventory, i.e., from receiving to shipping. Having less or improper understanding and visibility of your inventory, you can face major problems.
The problems include having too much stock that may reduce cash flow, and running out of stock can result in backorders that will make your customers disappointed and unhappy. That’s why having an effective warehouse management system will help you in improving the entire inventory management process. It will lead to quicker inventory turnover.
Improved security

Security is an essential factor to consider while managing a warehouse. There are so many warehouse management programs that employees need to use a single user account while entering different transactions. All these builds an audit trail that joins particular employees to do particular transactions. It will improve accountability and lessen down the theft risk and other such issues.
Also, it permits employers to find out new training courses and many different ways for employees to enhance their knowledge. In addition, all the user-based access level helps in preventing the unauthorized access for some reports and analysis. It will allow every user to access only that much information that is required for their work. You will not have to take tension regarding keeping company secrets and falling your competitive edge in this manner.
Enhanced relationships – Suppliers and Customers

An effectively running warehouse will always assist in decreasing lead times and order accuracy errors. The meaning of this lies in getting more and more customers getting satisfied with their orders. All these will result in getting more and more sales. When your team is ready and waiting to accept the orders of materials and supply chain, your partners can move towards the next task and fast delivery.
The warehouse management system handles the overall locations and inventory of your product. It has total system-driven efficiency that ultimately assists you in reducing the friction that you may feel with the supplier partners or with the end customers.
Best billing management

Many top warehouse management systems have built-in billing management tools. Some other have integrated or third-party app for offering the billing management feature. This feature helps the user use activity-based billing that has full capabilities to track all the activities in the warehouse similar to some suppliers and creates appropriate fees.
The WMS software helps in processing credit card payments and is united to massive e-commerce platforms.
Augment labour productivity

A feature-loaded warehouse management system is responsible for augmenting labor productivity. An unproductive warehouse and slow processing orders can cause significant issues like outdated stock and less motivation for the staff. For boosting the overall efficiency, it is vital to create modern systems and methods.
The warehouse management system has all the capabilities to optimize the flow of the stock with the help of an automated replenishment system for picking face stock. Also, the scanned picks offer a smooth link back to the software and then to the invoice or the transfer note.
8 Things To Look For In Your Next Warehouse Management System
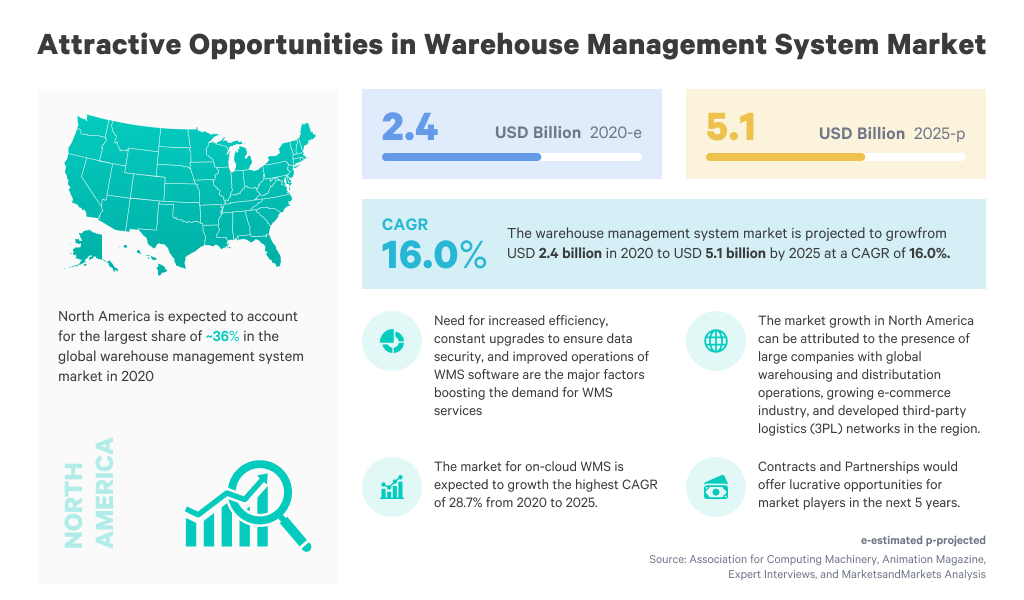
So you have made up your mind to purchase a warehouse management system? Let the experts be at your side! The demand for these dedicated software solutions is increasing with each passing year, and its market is estimated to touch $5.1 Billion by 2025. Since it is a strategic decision with long-term value and a direct impact on your business, it is necessary to weigh the pros and cons of different market offerings with respect to your organizational needs.
In this article, we will go through some of the most important points that you should look for when selecting your ideal solution. Let’s get started with the warehouse terminology and parameters that should form the basis of your evaluation in this eight-point mini-guide:
#1 Understand The Right Time To Seek A Warehouse Management Software
Every organization grows under unique conditions, and each of its business cases is bound to have an element of difference from its most identical competitor. This defines their internal processes, including sales, production, and procurement, which in turn determine the warehousing complexities.
Combining this with the coordination among your external stakeholders like 3PL service providers, the overall complexity level defines the right time to find yourself a warehouse management software.
Some of the common indicators are failing short of warehousing space despite having enough real estate, lack of inventory visibility, failing to utilize sitting inventory in time, and frequent errors during order picking on account of using excel to run warehousing operations.
#2 Define The Functionalities Needed In Your Ideal WMS Solution
Every sector has its own set of requirements when it comes to using warehouse technology. For instance, cold storage warehousing witnesses a relatively lower inventory turnover ratio, but the material handling best practices need to be followed with additional care. In the same way, you will need to develop a proper requirements scheme to find the best warehouse management software for your storage facility.
Try to include as much information as possible since it will help your prospective vendor’s sales representatives understand your inquiry. This can include the number of custom reports, fields required in them, deployment deadlines, dashboards, and functionalities.
#3 Involve The Core Teams In The Exploration And Feasibility Analysis Phase
One of the most common mistakes in procuring warehouse management technology is only consulting your IT team. Instead, you should keep the core business team that includes sales, production, and current warehousing staff members alongside your procurement and packaging teams in the loop.
They will give you a pragmatic view of which functionalities are needed, which will, in turn, help your IT team define the degree of customization needed. Also, the core team will be the ones using the software at different touchpoints, so comprehending their ability to use the same is equally essential. Involving the IT team on a standalone basis may do more harm than good.
#4 Explore The Solutions With Respect To Your Budget
Once you begin your buyer journey, you should explore solutions against your software requirements scheme (SRS) and your budget since many offerings are available in the market. Despite looking identical on the face value, you will find solutions with drastic pricing and capability differences.
It is advisable that you take a few demonstrations and even go ahead with a free trial of warehouse management software of your choice to explore the prospects. We also recommend you to go through their recurring charges such as AMC, customer support, and miscellaneous costs apart from the subscription and onboarding fees.
#5 Use The System Generated Reports To Evaluate The WMS Solutions
A great way of understanding whether a WMS solution is suitable for your business or not is to use system-generated reports. The number of data fields, their interconnection with other reports, departments, and processes, and the ease of making sense from them will give you a brief idea of how good the solution is.
In most cases, substandard software will provide you with generic reports that hardly reflect your needs. Also, you might find them erroneous in case the software isn’t working as expected. So look out for such signs to understand their feasibility.

#6 Analyse How Much Value Will The Software Deliver To Your Warehousing Operations
Some of the most important questions to ask yourself and your team are “How to improve warehouse management using this solution?”, “Does this software improve the operational efficiency, accuracy, and speed?” The answers to these questions from various stakeholders of your organization should be a significant decision-making factor.
Again, you should consider the learning curves, your staff’s proficiency in working with tech solutions, and the overall coordination of your team. All of these aspects also determine how successfully you can implement the WMS solution in your organization.
#7 Lookout For Existing Customer Portfolio And Coverage For Your Location
This is another important consideration, as having a vendor who serves a similar organization/sector can reduce the chances of any backfiring. Also, you should make it a point to contact non-competitors and see if any of your known organizations already use it.
The regional coverage also matters since the third-party integrations are among the top concerns once you start using a WMS solution. If you cannot integrate local companies’ software with yours, there’s practically no use of your WMS supporting even robotics in warehouse management.
#8 Check Out The Upscaling Capability And Costing
Lastly, we would like to draw your attention to the pricing structure and support for scaling up. Suppose you find that the subscription charges tend to inflate irrationally as you scale up, or ancillary/hidden costs create a large burden. In that case, it is in your best interests to abandon such solutions upfront.
This can be easily analyzed by comparing the upper cap on the number of integrations supported under each plan, the number of users, orders processed, and customer support. The pricing offset and technological capabilities are among the most crucial factors since you purchase WMS solutions to scale up in the first place.
Choosing a warehouse management solution for your business should be a calculated decision as it can have long-term implications for your firm. All activities carried out in your warehouse overlap with other departments and, ultimately, your revenue stream.
Weighing the pros and cons might require you to consult subject matter experts, but it is in your best interest to know the ins and outs before moving ahead with any vendor. We hope that this mini-guide helps you find the best warehouse management system for your firm.
Difference Between Inventory Management and Warehouse Management
Differentiating inventory management and warehouse management is a little complicated task. Let’s understand both in detail.
Warehouse Management System vs. Inventory Management System
Before starting to point out the differences between WMS and IMS, it is essential to know inventory management and warehouse management.
What is inventory management?

It is a set of processes dealing with supply chain management, inventory control, demand forecasting, and reverse logistics. Typically, inventory management is the first step that has been taken before warehouse management.
A list of tools that are involved in inventory management is economic order quantity, safety stock, cost of goods, inventory turnover, vendor-managed inventory, and customer-managed inventory.
The size of inventory management that is needed depends on every industry. Inventory management is considered the most effective strategy for small businesses as they understand its details and importance.
What is Warehouse Management?

It controls the storing and moving of materials and products that are present in the warehouse. These operations and processes are managed by an application or software known as a WMS (Warehouse Management System).
The role of WMS is to allow all the programs for centralizing the management of warehouse management processes like inventory tracking and stock locating.
The older WMS systems were not capable and feature-loaded, just like the current warehouse management systems, which are complex and need a whole team to run them.
Before we portray its differences, let’s see first some of the similarities between inventory management system and warehouse management system
The inventory management system and warehouse management system allow diverse companies to use barcoding devices to track different parts and products present in the warehouse.
The other features include monitoring product levels, packing, picking, and shipping items, receiving the order in the inventory, managing different locations, and performing cycle counts.
Inventory Management System VS Warehouse Management System
Complexity is one of the most notable differences between inventory management vs. warehouse management battle. There are many differences between these two, but this one is the highlighted difference.
Inventory management systems follow an easier and straightforward approach by providing the whole inventory at one location. On the contrary, warehouse management systems are complicated and separate warehouses in multiple sections and bins. It permits you to handle the complete storage system in the warehouse and not only at one fixed location.
Warehouse management systems let you discover particular items in the warehouse. Still, on the other hand, inventory management solutions will only inform you about the items present scattered in the warehouse. In addition, warehouse management is required for the continuing operations of different departments, different from inventory management.
As we had mentioned earlier, that complexity is one of the most highlighted differences between WMS and IMS, and now we will see below why
Complexity
Compared to WMS (Warehouse Management System), IMS (Inventory Management System) are simpler because they show a complete number of stock products or materials for all particular storage locations.
Warehouse management systems are little complex systems as they permit companies to handle their complete storage systems in one warehouse. Suppose the warehouse has different storage sections for the same product, then WMS can assist in handling all of them. Talking about IMS (Inventory Management System), they can only offer the information of the specific product presence.
Integrating capabilities
Here is another crucial difference between the inventory management system and the warehouse management system, i.e., integration capabilities. To what extent both of the systems can get integrated into the logistics of a company’s management and its supplies and inventory. Inventory management is the first task that takes place before the warehouse management process.
Warehouse management is more connected to other vital aspects of the company’s operations like sales and distribution, production supply, and quality management. We can say that warehouse management is indispensable for the existing processes in different departments, but inventory management does not cover this point.
Storing and controlling
Warehouse management provides you all of the specifics of inventory control, but inventory management offers you only quantity. Also, in an inventory management system, you can identify the products’ availability. On the other hand, inventory management in the warehouse depends on the usage of warehouse management that permits you to find out the particular locations to put the inventory or retrieve it.
Offered solutions by WMS and IMS
Warehouse management systems provide different business opportunities for analyzing and making adjustments in the inventory and storing when required. On the contrary, inventory management systems do not offer this kind of feature. Many valuable communication devices are being utilized in warehouse management systems to make all the variations and understand the inventory and products’ location—all these results in getting more and more efficient and smooth operations.
FAQs on Warehouse Management

There are always top frequently asked questions that are required to get appropriately answered. We have presented some of the most common and vital questions on warehouse management with their respective answers.
What is Warehouse Management?
Warehouse management can be defined as the diverse processes related to control and management of the warehouse of any business. There are so many steps in the process, i.e., it starts from incoming freight and moving an asset for tracking, managing logistics, and warehouse management in the warehouse. No matter there is one warehouse or many, businesses will handle all of the warehouse operations seamlessly.
What is WMS (Warehouse Management System)?
A WMS or Warehouse Management System is software built for controlling, recording, and automating different warehouse operations. The purpose is to boost the overall efficiency and productivity of any businesses’ warehouse operations. All these solutions are usually found as a standalone system. Many ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and SCM (Supply Chain Management) systems come with WMS modules covering the same features present in any standalone system.
What are some of the primary warehouse operations?
Warehouse operations take so much time and effort while working. This strategy is required when it is about having extra time-consuming processes. All these are the basic daily operations necessary to get done on time but take a lot of time in the whole process. The primary warehouse operations required to get done routinely comprise moving inventory, receiving inventory, making complete surety on the safe working condition and proper shipping.
What are the top features of the Warehouse Management System?
A WMS (Warehouse Management System) features include Warehouse Designing, Picking and Packing, Inventory Tracking, Shipping, Receiving and Putting-Away, Yard and Dock Management, Labor Management, and Reporting.
What are the main benefits of using a WMS (Warehouse Management System)?
The top benefits of using a Warehouse Management System cover –
Efficient Labor Allocation, Optimized Processes, Employee Morale, Reduced Operational Expenses, Enhanced Supplier and Customer Relationships, ERP Integration, Improved Inventory Balance, Transparency and Visibility, and Advanced Security and Safety.
What is the meaning of Logistics in Warehouse Management?
You might have heard this Logistic word before. But what is its role in warehouse management? It’s simple; logistics is a term used to describe different tasks related to warehousing, transportation, information management, inventory, etc.
When your different logistics functions work back to back, then only your supply chain will be productive. When your first goods’ transportation is scheduled right, they will arrive at the warehouse when the inventory room is present. When the goods leave the warehouse on time, they will reach their defined destination wherever needed.
What is Putaway?
Putaway is a straightforward process in warehouse management. It belongs to putting away your all kind of incoming stock. Also, the putaway process is a close part of inbound logistics that includes all sorts of tasks related to receiving inventory and stocking it.
A warehouse management system is highly beneficial for the efficient putaway. Many warehouse management system solutions offer complete assistance for storing stock and assigning it for storing.
#1 Rated Cloud ERP Software in USA
Get a big picture view of your business, without losing sight of the details. Cin7 Core makes enterprise-level inventory management, manufacturing, sales channel integration, reporting and more accessible to businesses of all sizes.
Start Free 14 Day Trial